Tor is an incredible power privacy enhancing tool that every security-conscious netizen should have in their arsenal. It doesn't replace a VPN service, since TOR isn't optimized for high bandwidth usage (like streaming music/videos) but it definitely has a place in my internet usage portfolio.
To use TOR, you need access to a small kit of software that includes the TOR router and the TOR browser (a locked down customized version of the Mozilla Firefox browser).
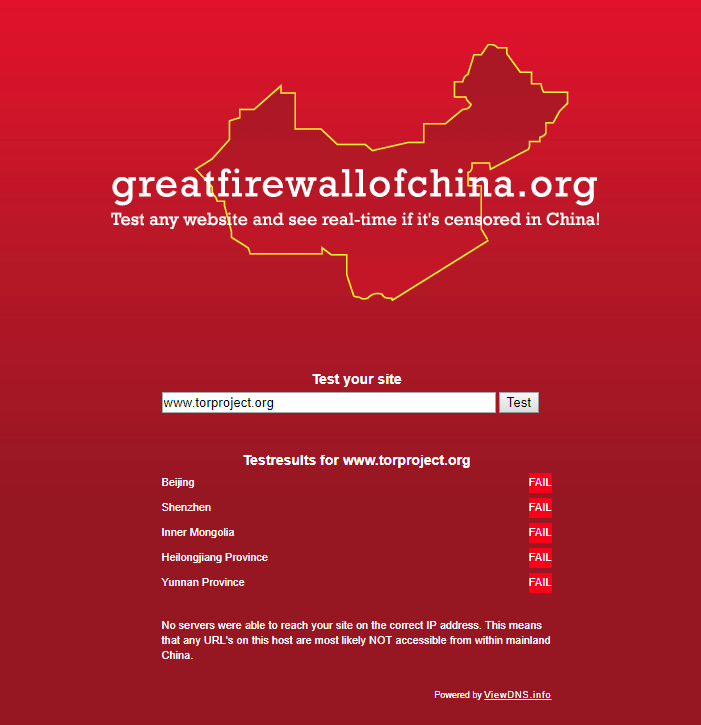
The Great Firewall of China site test tool confirms that the TOR Project website is blocked.
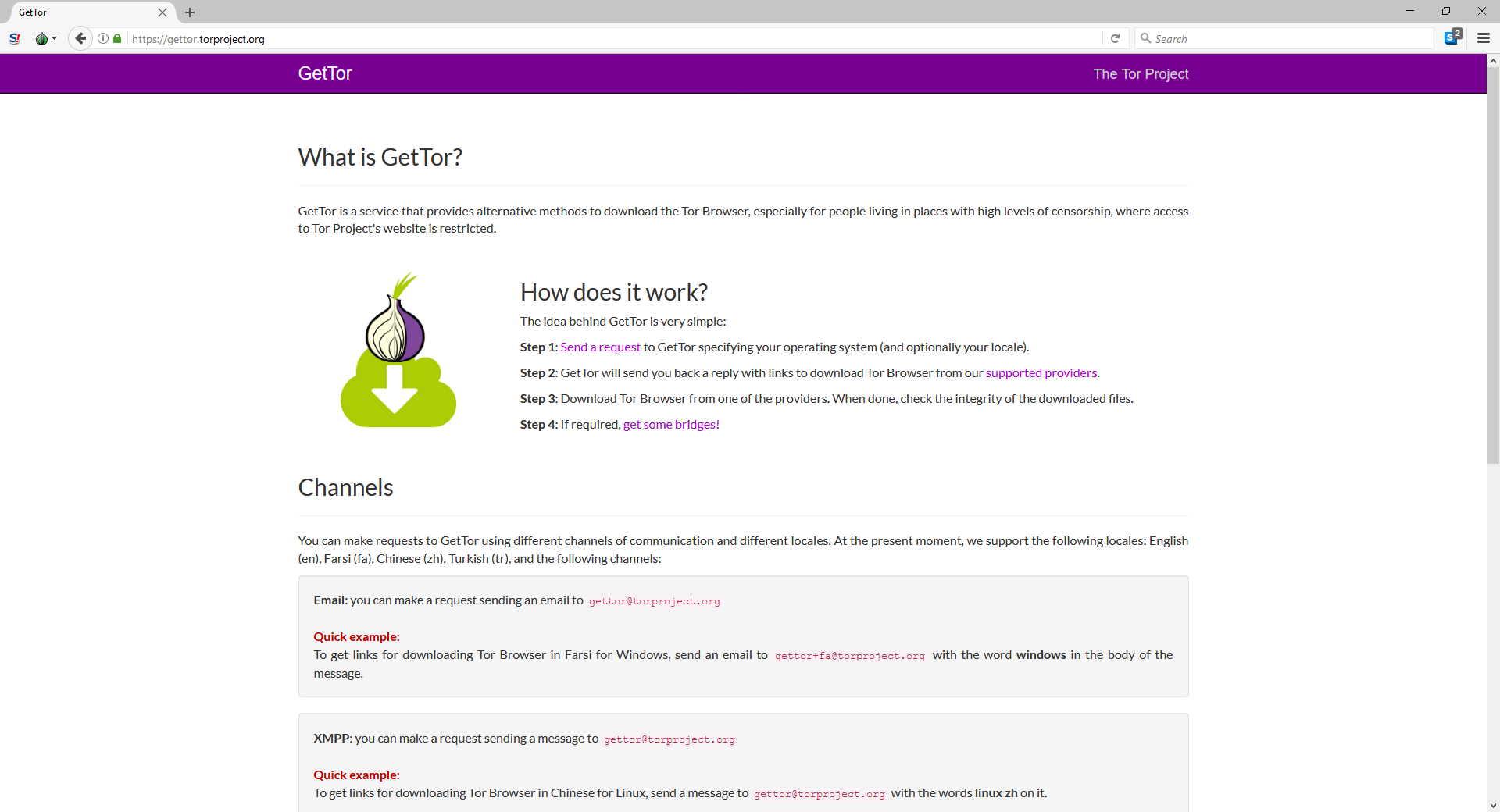
Luckily I live in Canada where we enjoy incredible internet freedom but what if you don't? What if you need TOR (because you live in a zone where the internet is tightly controlled or monitored) but you can't access the website to download the installer kit? The TOR project has create the GETTOR strategy to help those people gain access to its power network.
You can:
- Send an email to [email protected]
- Send an XMPP message to [email protected]
- Send a Twitter request (via DM) to @Get_tor
The system will then share with you a secret list of links to download the installer from GitHub, Dropbox or Google Drive.
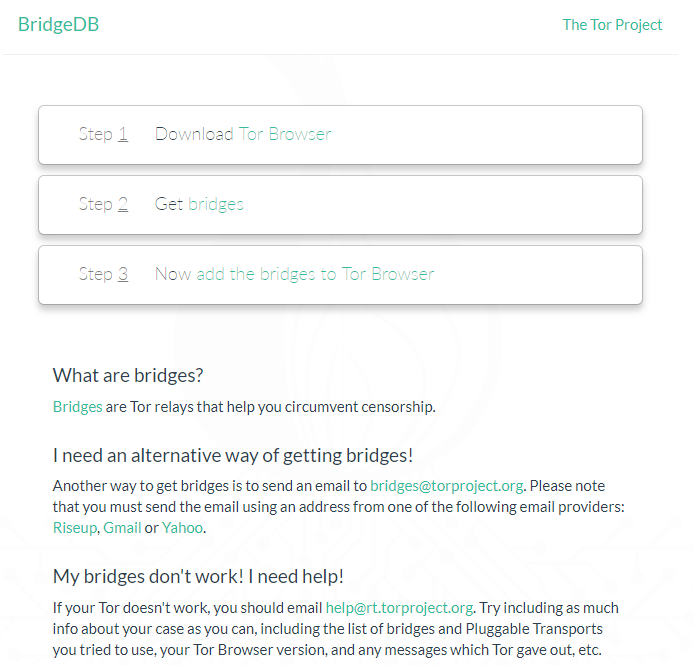
Once you install the TOR package (after checking the validity to ensure it hasn't been tampered with), you can also use a TOR Bridge if your country, school, company or ISP performs deep packet inspection to block TOR. A TOR bridge is a relay to help circumvent censorship.
You are now ready to enjoy private, anonymous and secure web browsing. Once installed, all future updates to the TOR software will be delivered via the TOR browser itself so you don't have to worry about performing these steps again.